
30 Aug Magnesium Wall Board Fire Rating Classification
Table of Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Fire Rating
- 3 Magnesium Oxide Boards and Fire Resistance
- 4 Material Comparison
- 5 Compliance and Installation
- 6 FAQ
- 6.1 What makes magnesium oxide boards different from regular drywall?
- 6.2 Can magnesium oxide boards be used outdoors?
- 6.3 How do magnesium oxide boards help meet building codes?
- 6.4 Are magnesium oxide boards safe for people with allergies?
- 6.5 Do magnesium oxide boards need special tools for installation?
Magnesium oxide boards get the highest fire rating classes, like Class A and A1, under ASTM E84, ASTM E136, and EN 13501-1 rules. These non-combustible MgO boards can handle fire at temperatures up to 1200°C and stay strong. Non-combustible MgO board does not catch fire, spread flames, or give off dangerous gases, which helps keep buildings safe from fire. Fire-resistant MgO boards give good protection for walls, ceilings, and floors. Non-combustible MgO boards follow tough fire safety rules, so they are important for meeting codes and keeping people safe. Builders pick non-combustible MgO boards for their great fire rating and for fire-resistant MgO board uses.
Key Takeaways
Magnesium oxide boards have high fire ratings like A1 and Class A. This means they do not burn or spread fire. They help keep buildings safe from fire. These boards pass big fire tests like ASTM E84 and EN 13501-1. They can stop fire for up to four hours. They also make very little smoke. Magnesium oxide boards are stronger than gypsum and cement boards. They are lighter and do not get damaged by water or mold. They last longer in fires too. Builders use magnesium oxide boards in many walls, ceilings, and floors. These boards meet strict building rules and are simple to put in. If you install them right and check fire certifications, they give the best fire safety.
Fire Rating
A1 and A2 Classification
A1 and A2 fire ratings are the best for building safety in Europe. These ratings come from the EN 13501-1 standard. This standard checks how materials act when there is a fire. A1 is the highest fire rating. Materials with an A1 rating do not help fires grow at any time. They do not burn or spread flames. They also do not add to the fire, even in big fires. Builders use A1-rated materials like stone, brick, and magnesium oxide board. These materials have less than 1% organic matter. They give the best safety and help protect buildings for a long time.
A2-rated materials also follow strict fire safety rules. They are non-combustible and do not make fires worse or faster in a big fire. But A2 materials might help a fire a little more than A1. Some examples are glass fibers, gypsum boards, and some sandwich panels. Both A1 and A2 ratings meet building codes and fire rating standards. But A1 gives more safety. There is usually no big price difference between A1 and A2 products. Many builders pick A1 for the best fire safety.
The table below shows the main rules for A1 and A2 fire ratings under EN 13501-1:
Fire Rating | Key Tests | Criteria/Thresholds |
|---|---|---|
A1 | Non-combustibility test | Temperature rise ≤ 30°C; Mass loss ≤ 50%; No sustained flaming |
| Gross heat of combustion test | Gross calorific potential < 2.0 MJ/kg |
| Notes | Materials with <1% organic content can be A1 without testing |
A2 | Non-combustibility or combustion | Temperature rise ≤ 50°C; Mass loss ≤ 50%; Flaming ≤ 20 s OR calorific ≤ 3.0 MJ/kg |
| Single burning item test | Fire growth rate ≤ 120 Ws⁻¹; Lateral flame spread < specimen edge; Heat ≤ 7.5 MJ/10m |
A1 and A2 fire rating rules help builders pick the safest wall boards. Magnesium oxide boards often get A1, so they are a top choice for better fire ratings and fire resistance.
ASTM and EN Standards
Fire rating standards tell how to test and sort wall boards for fire safety. The most important standards are ASTM E84, ASTM E119, and EN 13501-1. Each one checks a different part of fire safety.
ASTM E84: This standard checks how fast flames and smoke move on a board’s surface. The test uses a tunnel furnace to burn the board. Boards with low flame and smoke scores get a Class A fire rating. Magnesium oxide boards often get a perfect 0/0 score. This means no flame spread or smoke.
ASTM E119: This standard tests how well wall, floor, and ceiling assemblies resist fire. It burns the whole assembly for a set time. The test checks if the assembly stays strong and blocks fire. Magnesium oxide boards can pass ASTM E119 for up to four hours. This shows great fire resistance.
EN 13501-1: This European standard uses many tests to sort materials from A1 (non-combustible) to F (no data). It checks heat, flame spread, smoke, and fire growth. Magnesium oxide boards often get the A1 rating, which is the best for fire safety.
The table below compares these fire rating standards:
Standard | Focus Area | Test Method | Key Parameters / Classification | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ASTM E84 | Surface Burning | Tunnel furnace test | Flame spread index, smoke developed | US standard for reaction to fire |
ASTM E119 | Fire Resistance | Furnace exposure of assemblies | Structural integrity, insulation, duration | Measures fire endurance of assemblies |
EN 13501-1 | Reaction to Fire | Multiple tests (calorific, SBI test) | A1 (non-combustible) to F (no data) | Comprehensive EU classification for fire safety |
Magnesium oxide boards do very well in these tests. They get the best fire ratings under both ASTM and EN standards. These boards do not burn or spread flames. They do not make smoke. They also let out water vapor during a fire. This helps cool and slow down the flames. This special feature makes magnesium oxide boards safer than other wall boards.
Note: Builders should always check fire rating standards before picking wall boards. Using boards with high fire ratings, like magnesium oxide boards, makes buildings safer and helps meet building codes.
Magnesium Oxide Boards and Fire Resistance
 Zero Flame Spread
Zero Flame Spread
Magnesium oxide boards are very good at stopping fire. They have special parts like perlite, vermiculite, and glass fiber mesh. Perlite is a light volcanic glass that helps keep heat out and makes the board lighter. Vermiculite gets bigger when hot and forms a shield against fire. Glass fiber mesh makes the board stronger so it does not break from heat. The way the boards are made helps them stay fire-resistant.
Magnesium oxide has a melting point of about 2800°C. This means the boards do not lose their shape in strong fires. The chemical bonds in magnesium oxide are strong and do not burn. These boards are non-combustible mgo materials. They do not catch fire or make dangerous gases, even at 1200°C. The minerals in the board soak up heat and slow down flames.
Magnesium oxide boards got a zero flame spread index and zero smoke index in ASTM E84 tests. This puts them in the top fire safety group, called Class A1. In real fires, these boards do not catch fire or help flames grow. This makes them great for fire-rated walls and ceilings.
Here are reasons why magnesium oxide boards stop flames:
Non-combustible mgo keeps the board from burning.
High heat stability keeps the board strong in fire.
The board soaks up heat and slows fire down.
No flames show, even in very hot fires.
Fiberglass mesh makes the board tough and hard to break.
These things make fire-resistant mgo boards a top pick for walls, ceilings, and room dividers in homes and businesses.
1-Hour and 2-Hour Ratings
Magnesium oxide boards pass 1-hour and 2-hour fire tests easily. In ASTM E119 tests, these boards stay strong for up to four hours. This is better than what most building rules ask for, which is usually only 1 or 2 hours.
Fire-resistant mgo boards do not need water inside to stop fire, unlike gypsum boards. Their minerals and non-combustible mgo binder keep them from burning or getting weak in long fires. Even in high heat, the boards keep their shape and stop fire and smoke from spreading.
The table below shows how magnesium oxide boards compare to other boards:
Board Type | Fire Resistance Performance |
|---|---|
Magnesium Oxide Boards | Very fire-resistant; does not burn; lasts 1-2 hours or more; stays strong |
Gypsum Board | Fire-resistant but needs water inside; usually lasts 30 minutes to 1 hour |
Cement Board | Not as fire-resistant as MgO; can get weak in heat; may need extra help |
Magnesium oxide boards meet many fire safety rules like EN 13501-1, ASTM E119, UL 263, and BS 476 Part 4. These boards help keep fire in one area, so people can get out safely and fire does less damage. Fire-resistant mgo boards do not need extra fireproofing, so they are easy to use and save money.
Fire-resistant mgo boards are better at stopping fire than gypsum or cement boards. Their non-combustible mgo, strong heat resistance, and ability to stay strong make them the best for fire-rated walls in new buildings.
Material Comparison
MgO vs. Gypsum
Magnesium oxide boards and gypsum boards are both used for fire-rated walls. But they do not work the same way in a fire. Magnesium oxide boards can meet fire safety rules at just 3 mm thick. Gypsum boards need to be 12 mm thick to do the same job. Magnesium oxide boards can handle heat up to 800°C and still keep their shape. Gypsum boards do not burn, but they do not last as long in a fire. They can break down faster.
Attribute | Magnesium Oxide Board | Gypsum Board |
|---|---|---|
Fire Resistance | Meets fire resistance standards at 3 mm thickness | Requires 12 mm thickness to meet fire resistance standards |
Criteria | Magnesium Oxide (MgO) Boards | Gypsum Boards |
|---|---|---|
Fire Resistance Rating | Up to 4 hours (A1 Non-Combustible) | Limited, typically less than 1 hour (Fire-Resistant but Combustible) |
Thermal Combustibility | Non-Combustible | Combustible |
Flame Spread | Zero Flame Spread | Moderate Flame Spread |
Fire Endurance | Very High | Limited |
Magnesium oxide boards make very little smoke and no toxic gases in a fire. Gypsum boards make more smoke and get weak faster. Magnesium oxide boards stop flames from spreading and protect better in fire-rated walls.
MgO vs. Cement Board
Magnesium oxide boards are better than cement boards for fire safety. Both types do not spread flames much. But magnesium oxide boards stay strong and keep their shape in high heat for up to four hours. Cement boards might need extra help to handle fire. Magnesium oxide boards are lighter and easier to put up. Cement boards are heavier and harder to cut.
Property | Magnesium Oxide (MgO) Board | Cement Board |
|---|---|---|
Fire Resistance Rating | A1 Non-Combustible; excellent fire resistance | Moderate fire resistance; may need treatments |
Fire Duration Resistance | Up to 4 hours maintaining strength and shape | Handles fire but may require extra support |
Flame Spread | Low flame spread | Low flame spread |
Smoke and Toxic Gas Emissions | Low emissions; minimal smoke and toxic gases | Low emissions but generally higher than MgO |
Performance in High Heat | Maintains strength and shape under extreme heat | May require additional fireproofing |
Installation Ease | Lightweight and easier to install | Heavier and harder to install |
Suitability for Fire-Rated Applications | Preferred for high fire-risk areas due to superior fire resistance and low smoke emission | Suitable for lower fire risk or less extreme heat environments |
Some magnesium oxide boards have magnesium chloride. This can cause water problems and rust in wet places. Newer magnesium sulphate boards are more stable. Cement boards and calcium silicate boards are good at handling water and last a long time. This makes them good for tough fire-rated walls.
Fire-Rated Walls Applications
Magnesium oxide boards are used in many fire-rated walls and enclosures. Big buildings like hospitals, schools, hotels, offices, and apartments use these boards to meet fire rules. Builders put magnesium oxide boards in fire walls, ceilings, and other fire-resistant places. These boards do not burn or let flames spread. They also do not get damaged by water or mold, so they work well in busy areas.
Provide support for interior and exterior coverings
Serve as a foundation for flooring and subflooring
Suitable for structural insulation panels in commercial construction
Applied in prefabricated modular buildings
Magnesium oxide boards have many good points over other fireproof materials. They stay strong in high heat, are light, and do not get damaged by water or mold. These boards do not give off harmful gases in a fire. This makes them a safer choice for fire-rated walls.
Advantage Category | Magnesium Oxide (MGO) Board | Other Materials (Gypsum, Concrete, Fiberglass, etc.) |
|---|---|---|
Fire Resistance | Maintains structural integrity at temperatures >1,000°F for over 2 hours; superior to gypsum which fails sooner | Gypsum loses effectiveness under prolonged heat; concrete resists fire well but is heavy; fiberglass may melt or deform |
Weight and Handling | Lightweight, facilitating easier handling and faster installation, reducing labor costs | Concrete is heavy and slower to install; gypsum and cement boards are heavier than MGO |
Moisture and Mold Resistance | Resistant to moisture, mold, and mildew, extending durability and reducing maintenance | Gypsum and some other materials are more susceptible to moisture damage and mold growth |
Emissions under Fire | Does not emit harmful gases when exposed to high temperatures | Some traditional materials release toxic gases during fire exposure |
Environmental Impact | Made from abundant natural resources; free of harmful chemicals and VOCs; recyclable; lower energy manufacturing | Other materials may have higher energy consumption and less recyclability |
Installation Ease | Requires fewer tools; easy to cut and shape; quicker installation process | Traditional materials may require specialized tools and more labor |
Durability | Resistant to termites and moisture, leading to longer-lasting installations | Some traditional materials require more frequent replacement or repair |
Magnesium oxide boards give better fire protection, are easy to install, and last a long time. This makes them a top choice for fireproof walls in homes and businesses.
Compliance and Installation
Building Codes
Magnesium oxide boards follow tough fire safety rules in many places. These boards do not burn and pass ASTM E136 tests. They have certificates from CCRR, Intertek, and ICC-ESR. These show the boards meet International Building Code (IBC) for Types I and II buildings. Magnesium oxide boards stay strong for four hours in fire, even at 1,472°F. They do not make toxic fumes during fire, so people inside are safer. These boards get an A1 non-combustible rating and do not help fire spread. Builders use them in homes and businesses to meet fire safety codes.
Third-party certificates help builders and inspectors trust magnesium oxide boards for fire-rated walls.
Purpose/Description | |
|---|---|
EN 13501-1 (Class A1 Noncombustible) | Top fire resistance; does not add to fire, little smoke or fumes |
ASTM E136 | Shows board does not burn |
ASTM E84 | Class A rating for surface fire spread |
ICC-ES ESR-2880 | Proves board meets building codes |
INTERTEK and ILAC-MRA | Lab approval for use worldwide |
Moisture Resistance
Magnesium oxide boards are very good at keeping water out. Their smooth surface stops water, so boards do not swell or get weak. This helps the boards stay fire-resistant for a long time. Even in wet places like bathrooms or basements, the boards do not bend or break. They also stop mold, mildew, and rot, so boards last for years. The boards keep their fire rating for 1 to 4 hours, even when wet. Builders can use magnesium oxide boards in dry or wet places without losing fire safety.
Practical Use in Fire Assemblies
Installing magnesium oxide boards the right way is important for fire safety. Builders should use screws that do not rust and space them 12 to 16 inches apart. They need to overlap seams by one inch and use tape and compound for smooth joints. Holes for wires or pipes must be cut with care, and all local rules must be followed. Boards should be kept flat and dry and left in the room for two days before use. Builders should leave small gaps between boards and use soft fillers to stop cracks from movement or heat changes.
Installation Step | Details |
|---|---|
Fastening | |
Joint Handling | Overlap seams; use tape and compound. |
Board Acclimation | Let boards sit in room for 48 hours. |
Cutting Tools | Use strong knives or saws; wear safety gear. |
Storage |
Tip: Always follow fire safety rules and local codes when installing to keep boards working well against fire.
Knowing about fire rating helps builders pick the right board. Magnesium oxide boards get A1 fire ratings. They stay strong in high heat. They do not make toxic smoke. The table below shows important features:
Test/Property | Result/Description |
|---|---|
ASTM E84 Flame Spread | |
Fire Resistance Duration | 30 minutes to 2 hours in walls and ceilings |
Non-Combustibility | Does not burn or contribute to fire spread |
Smoke and Toxicity Emission | No harmful gas release |
Builders should look at different boards and check certifications. MgO boards are better than gypsum and cement boards. They are safer, resist water, and last longer. Good installation and following rules help boards protect against fire.
Tip: Pick a board that meets fire safety codes. Make sure it fits the building’s needs. MgO boards help keep buildings safe from fire.
FAQ
What makes magnesium oxide boards different from regular drywall?
Magnesium oxide boards stop fire, water, and mold. Regular drywall does not protect as well from fire. Builders pick these boards when they need more safety and strength.
Can magnesium oxide boards be used outdoors?
Yes, these boards work well outside in all weather. They do not get damaged by rain or wet air. Builders use them for outside walls, soffits, and siding.
How do magnesium oxide boards help meet building codes?
These boards pass hard fire tests like ASTM E84 and EN 13501-1. They count as non-combustible materials for buildings. Builders use them to help projects follow local and world rules.
Are magnesium oxide boards safe for people with allergies?
Magnesium oxide boards do not let mold or mildew grow. They do not give off bad gases. People with allergies or asthma can use these boards at home or work.
Do magnesium oxide boards need special tools for installation?
No, builders can cut and put up these boards with normal tools. The boards are light and simple to move. This makes it quicker and safer to install them.
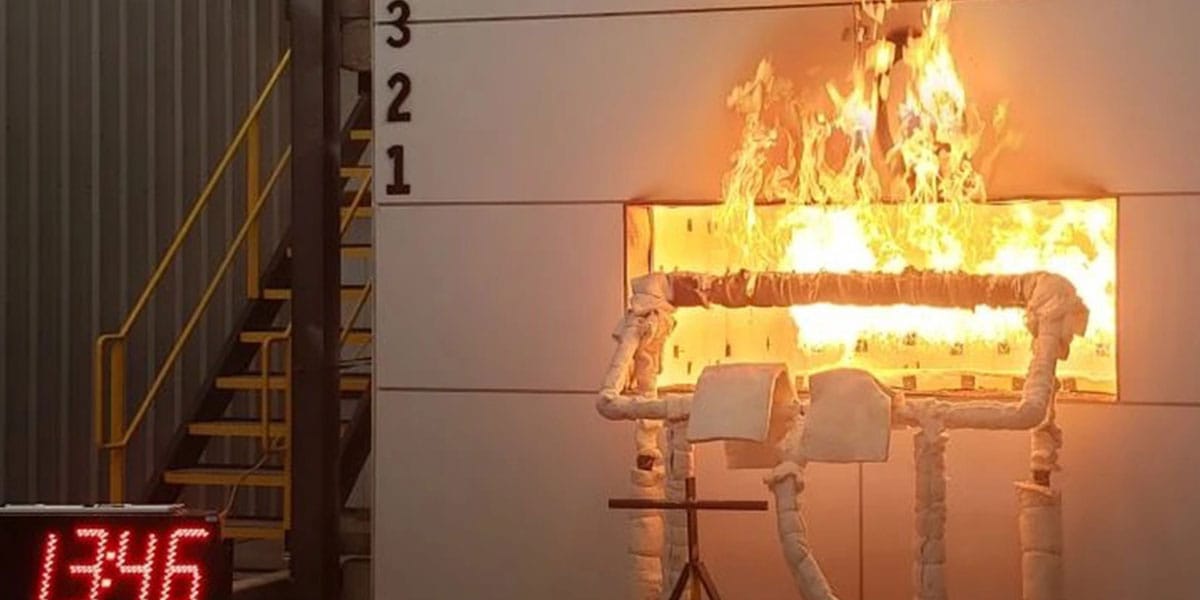
 Zero Flame Spread
Zero Flame Spread