26 Aug Understanding the Role of Magnesium Wall Boards in Hospital Fire Safety
Table of Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Fire Safety
- 3 Fire Code Compliance
- 4 Material Comparison
- 5 Practical Use
- 6 FAQ
- 6.1 What fire ratings do magnesium wall boards achieve in hospitals?
- 6.2 Are magnesium wall boards safe for wet hospital areas?
- 6.3 How do magnesium wall boards compare to gypsum boards for fire safety?
- 6.4 Do magnesium wall boards require special installation tools?
- 6.5 Can magnesium wall boards help reduce hospital maintenance costs?
Hospitals require walls that ensure fire code compliance and keep people safe during fires. Magnesium oxide boards outperform regular gypsum wallboard in several important ways:
Property | Magnesium Oxide Board (MgO) | Traditional Gypsum Wallboard |
|---|---|---|
Fire Resistance | A1 non-combustible; does not burn or emit fumes | Slows fire spread; less heat resistance |
Maximum Heat Resistance | Up to 1200°F | Lower heat resistance |
Moisture Absorption | 0.34% (very low) | About 3% (higher) |
Mold and Mildew Resistance | Resists mold and mildew | Can support mold growth |
These characteristics help hospitals maintain strict fire code compliance while enhancing building strength and safety. Facility managers often inquire about how these boards perform in real-world conditions, what fire safety standards they meet, and how they integrate into the daily operations of a hospital.
Key Takeaways
Magnesium wall boards can stop fire for 4 hours. They do not burn or make dangerous smoke. This helps keep hospitals safe when there is a fire. These boards also stop water, mold, and pests. This means hospitals need less fixing and the air stays cleaner inside. Magnesium boards pass tough fire safety tests and rules. This makes sure they work well in real hospitals. You can put them in with normal tools. It is important to use the right steps and rust-proof fasteners for safety. Magnesium boards cost more than gypsum boards. But they last longer and need fewer repairs, so they save money later.
Fire Safety
Fire-Resistant Properties
Magnesium wall boards are very good at stopping fires in hospitals. Tests show these boards do not burn or help fire spread. Their minerals make them noncombustible, so they meet top fire safety ratings like Class A and A1. The boards can handle heat up to 1200°C and keep their shape and strength during a fire. This gives people more time to leave safely and helps stop buildings from falling down.
Fire-Resistant Property | Description | Fire Safety Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Noncombustibility | Does not burn or support fire spread | Stops flames and meets Class A, A1 ratings |
High Temperature Performance | Withstands heat up to 1200°C; melting point ~2800°C | Maintains integrity, prevents collapse, allows evacuation time |
Smoke and Toxicity Emissions | Produces no harmful gases or smoke | Reduces toxic exposure, enhances occupant safety |
Structural Integrity | Remains strong under fire exposure | Supports fire-rated walls and ceilings for up to 2 hours or more |
Fire Test Compliance | Passes ASTM E84, ASTM E119, EN 13501-1+A1:2010 | Achieves top fire ratings, confirms superior fire resistance |
Magnesium wall boards can resist fire for one to four hours. This depends on how thick the boards are and how they are put in. When there is a fire, the boards form crystals that make them stronger. Magnesium wall boards do not need extra coatings to be fire-resistant. They do not catch fire or let flames spread, so hospitals can follow fire safety rules.
Hospital Applications
Hospitals use magnesium wall boards in important places to help stop fires. Facility managers put these boards in busy hallways, entrances, and shared spaces. The boards are used for walls and ceilings that need to be fire-rated. Bathrooms and wet areas also use these boards because they resist water and mold.
Corridors and entries
Common areas
Fire-rated walls and ceilings
Bathrooms and high-humidity zones
Magnesium wall boards are tough and can handle bumps, so they work well in busy hospital areas. Hospitals add these panels during renovations to make fire safety better. The boards work with fire alarms and sprinklers to keep everyone safe. They stay strong even in very hot fires, which makes them better than regular drywall or plywood. Hospitals trust magnesium wall boards to help meet fire codes and protect people for a long time.
Fire Code Compliance
 Standards and Certifications
Standards and Certifications
Hospitals must follow strict rules to keep patients and staff safe from fire. Wall boards in these buildings need to meet several important standards and certifications. These rules help ensure that every part of a wall, not just the board itself, works together to stop fire and smoke.
Fire-rated hospital walls must be tested as complete assemblies. This includes studs, tracks, joints, screws, and finishing compounds.
ASTM E119 (also known as UL 263) checks the fire resistance of the whole wall system. For a one-hour rating, the wall must hold back fire for at least one hour.
ASTM E84 (UL 723) measures how fast flames and smoke spread. Hospitals need Class A fire-rated finishes, which means the wall does not let fire or smoke move quickly.
Class A ratings are required for new hospitals built after July 5, 2016.
Proper installation is critical. If workers do not follow the tested assembly instructions, the wall may not pass fire code compliance checks.
Note: Wall boards must also have independent third-party certifications. Groups like Underwriters Laboratories (UL) and the British Board of Agrément (BBA) test and certify magnesium wall boards. The BBA is trusted worldwide and checks that boards meet fire safety and building standards.
NFPA 285 and ASTM E84
Magnesium wall boards must pass tough fire tests to be used in hospitals. Two of the most important tests are NFPA 285 and ASTM E84.
NFPA 285 checks how fire spreads on walls with windows and other openings. Magnesium wall boards meet this standard, showing they do not let fire move up or across the wall.
ASTM E84 measures flame spread and smoke development. Magnesium wall boards often score 0/0, which means they do not let flames or smoke move at all. This is the best possible result and meets Class A requirements.
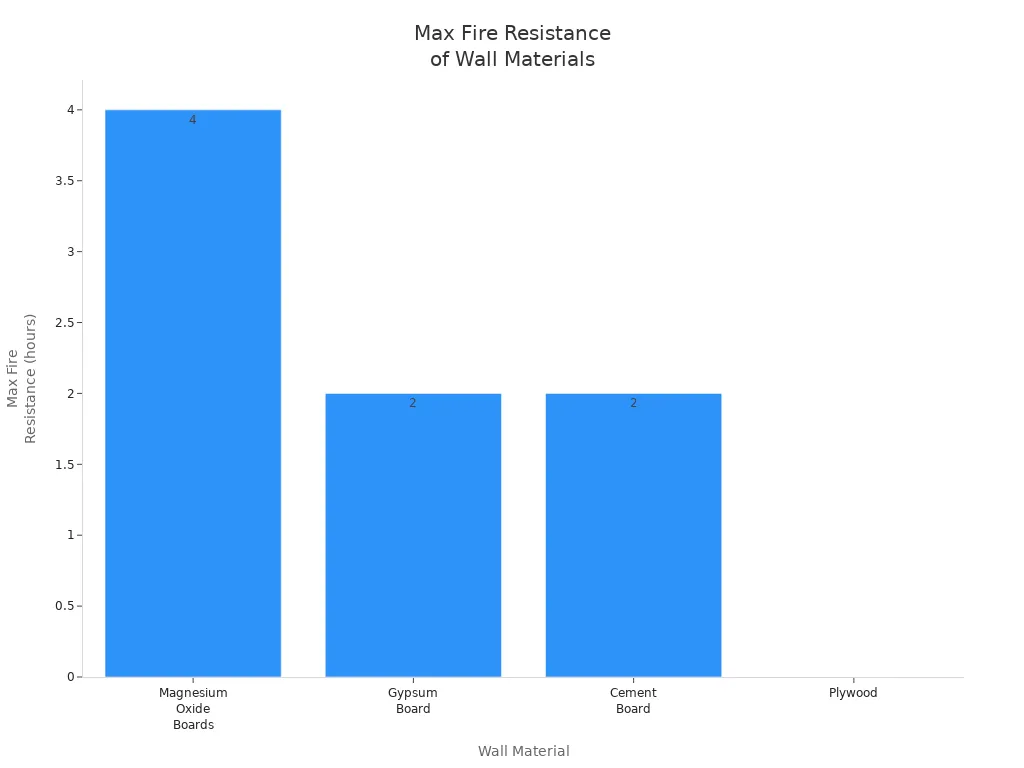
Material | Fire Resistance Rating (Hours) | Combustibility | Smoke/Toxic Fumes |
|---|---|---|---|
Magnesium Oxide Boards | Non-combustible | None | |
Gypsum Board | 0.5 to 2 | Combustible | Low smoke |
Cement Board | 1 to 2 | Non-combustible | None |
Plywood | 0 | Combustible | Produces smoke |
Magnesium wall boards also pass EN ISO 1716 and EN 13501 tests. These results confirm that the boards do not burn, do not make smoke, and help cool fires by releasing water vapor.
Verified Performance
Hospitals cannot rely on claims alone. They need proof that magnesium wall boards will work in a real fire. Verified performance comes from third-party testing and certifications.
Independent labs test the boards for fire resistance, smoke, and toxic gas release.
Some magnesium wall boards, like Suparna MgO and MagPanel®, have A1 or Class A ratings. These ratings mean the boards are noncombustible and safe for hospital use.
Not all magnesium wall boards pass every test. In 2020, some brands failed the ASTM E136 noncombustibility test. This led to the loss of important certifications and warnings from building code groups.
Hospitals should always check for up-to-date certifications and test results before choosing a product.
Product thickness and manufacturing quality also matter. Thicker boards usually resist fire longer. High-quality boards keep their strength and do not release harmful gases when hot. Proper installation, with the right fasteners and sealed joints, helps the wall meet fire code compliance.
Tip: Always ask for third-party test reports and certifications before using magnesium wall boards in hospital projects. This helps ensure fire code compliance and keeps everyone safe.
Material Comparison
MgO vs. Gypsum Board
Magnesium oxide boards and gypsum boards are both used in hospitals. But they are different in some important ways.
MgO boards are better at stopping fires because of their minerals. They stay strong even when it gets very hot, up to 750°C.
MgO boards pass hard fire safety tests like ASTM E119 and EN ISO 1716. These tests show that MgO boards do not burn and last longer in a fire.
Gypsum boards slow down fire by letting out water inside them. But this only works until the water is gone.
Gypsum boards can stop fire for about 51 to 79 minutes. This depends on how thick they are and how many layers there are. They must also pass ASTM E119 and other tests.
MgO boards can stop fire for up to 4 hours. They have many world certifications, so they are better for hospital areas with more risk.
Gypsum boards cost less and are good for normal building jobs. But MgO boards are better at stopping water and fire, which is important in hospitals.
Material Type | Average Cost per Square Foot |
|---|---|
Magnesium Sulfate (MgO) Boards | |
Gypsum Boards | $0.50 – $1.00 |
MgO boards cost more at first. But they last longer, stop fires better, and need less fixing. This can save hospitals money over time.
MgO vs. Cement Board
MgO boards and cement boards both help stop fires. But MgO boards have some extra good points for hospitals.
MgO boards do not burn and can take heat up to 1200°C. They do not break down in fire.
MgO boards do not soak up water or let mold grow. Cement boards can bend or break if they get wet.
MgO boards are lighter and easier to put up. You do not need special tools or lots of workers.
Cement boards are strong and stop fire, but they do not stop mold as well as MgO boards.
In hospitals, MgO boards help keep things clean and lower the need for repairs. They do not take in water or let mold grow.
Property | MgO Boards | Cement Boards (Fiber Cement) |
|---|---|---|
High (up to 1200°C) | High (less than MgO) | |
Moisture Resistance | Excellent | High (less mold resistant) |
Mold Resistance | Excellent | High |
Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
Installation Ease | Easy | Moderate |
Advantages and Limitations
MgO boards have many good things for building hospitals.
MgO boards can stop fire for up to 4 hours. They do not soak up water or let mold grow. They also help keep the air clean. Their thick build helps keep noise down, which is good in busy hospitals.
They are light, easy to put up, and made from safe, green materials.
MgO boards do not let bugs or termites in, so there is less damage.
But they cost more than gypsum or cement boards. Sometimes, you cannot find them in every place.
In very wet places, some MgO boards can get weaker. Magnesium oxysulfate boards work better in wet places and do not let fungus grow.
Advantage / Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
Fire Resistance | Up to 4-hour fire ratings, critical for hospital safety. |
Water and Mold Resistance | Absorbs little water, resists mold, improves air quality. |
Pest Resistance | Resists termites and mold, lowers maintenance. |
Lightweight | Easier handling and installation. |
Soundproofing | Reduces noise in hospital areas. |
Environmental Benefits | Made from sustainable, non-toxic materials. |
Higher Initial Cost | More expensive than gypsum or cement boards. |
Limited Availability | Not always available in all regions. |
Some types lose strength in high humidity. |
Hospitals should think about these things when picking wall boards. This helps keep people safe, makes buildings last longer, and saves money in the long run.
Practical Use
 Installation
Installation
Putting in magnesium wall boards the right way keeps hospitals safe from fire. It also helps the boards last a long time. Facility teams use these steps to install the boards:
Let boards get used to the room’s temperature and humidity for two days before putting them up.
Carry boards on their sides. Stack them flat on wood or mats so they do not bend.
Use joists to hold up the ends of the boards.
Leave a small gap, about 1/8 inch, between boards and walls so they can expand.
Pick screws that do not rust, like 316-stainless steel or ceramic-coated ones.
Use the right screws for wood or metal studs.
Put screws every 6 inches around the edges and every 12 inches in the middle.
Place screws at least 4 inches from corners and about half an inch from the edge.
Start screwing from one side and move across the board to keep it from cracking.
Cut boards with special knives or saws with carbide tips. Do not use power saws inside.
Fill the seams with polyurea or epoxy to make the surface smooth.
Wear a dust mask and safety glasses when cutting or sanding.
Put a barrier between the boards and galvanized steel frames.
Follow all building codes for your area.
Magnesium wall boards come in strong packaging so they do not get damaged while moving or storing. Workers handle the boards carefully to keep them in good shape.
Maintenance
Magnesium wall boards are easy to take care of in hospitals. They do not soak up much water, so they do not swell or grow mold. You do not need to seal them to keep out water, which saves money. Cleaning is simple; just wipe with a damp cloth. Bugs and rodents do not like the boards, so pest problems are less.
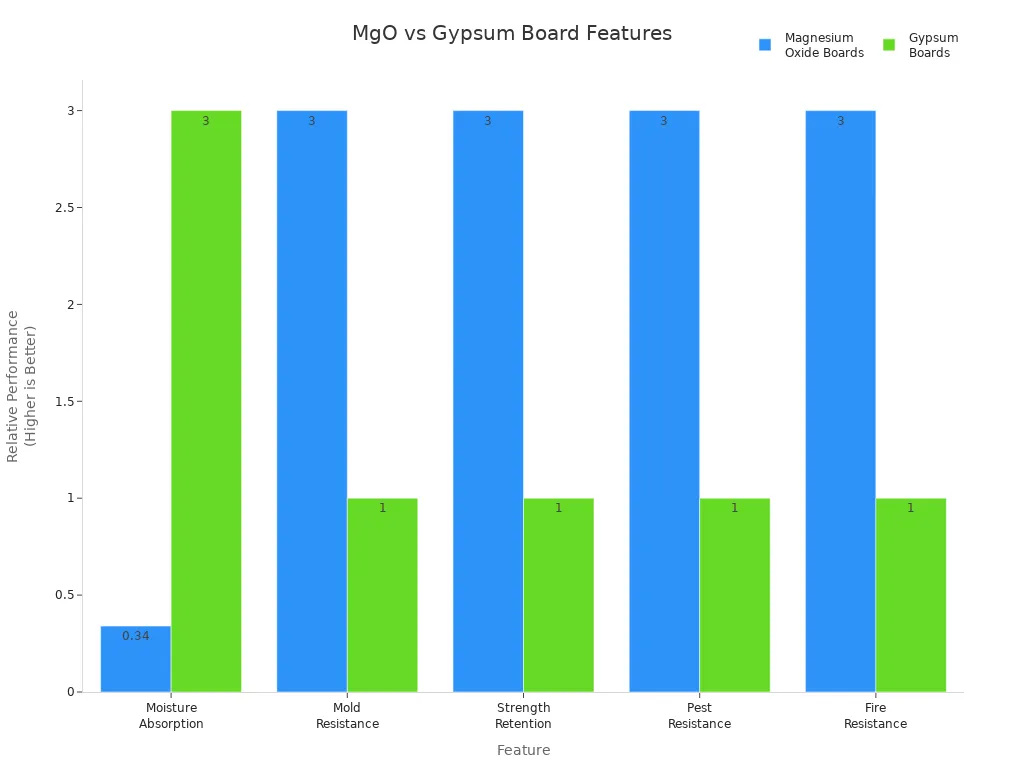
Feature | Magnesium Oxide (MgO) Boards | Gypsum Boards |
|---|---|---|
Moisture Absorption | Higher (about 3%) | |
Mold Resistance | High (stops mold growth) | Low (can get mold) |
Strength Retention | Stays strong when wet | Gets weak or cracks |
Pest Resistance | No bugs or rodents | Not listed |
Fire Resistance | Passes tough fire tests | Not listed |
Real-World Performance
Reports from hospitals show magnesium wall boards work well in busy places.
MagPanel® boards do not break easily and stay strong even when hit.
Hospitals say the boards do not get weak in humid rooms.
The boards stop mold, mildew, fungus, and allergens from growing.
They do not burn, termites cannot eat them, and they keep their shape.
Hospitals use MagPanel® for walls and ceilings because it works well.
The boards have a five-year warranty for any big problems.
Reports say magnesium boards help keep hospitals clean and safe for a long time.
Magnesium wall boards help hospitals stay safe, clean, and strong for patients and workers. Facility managers trust these boards because they last long and need little care.
Magnesium wall boards help keep hospitals safe from fire. They are strong and do not get damaged by water. These boards also last a long time. Experts test them to make sure they meet tough rules. This helps hospitals save money over time. Fire safety experts give these tips:
Pick boards with Class A ratings and the right thickness.
Use fasteners that do not rust and follow the rules for putting them in.
Do not let the boards get wet for a long time. Use coatings if the boards are outside.
Always follow local building codes and safety rules.
Hospitals get good fire protection, less work fixing walls, and cleaner air inside.
FAQ
What fire ratings do magnesium wall boards achieve in hospitals?
Magnesium wall boards usually get Class A or A1 fire ratings. These ratings mean the boards do not burn or make harmful smoke. Hospitals use these ratings to help keep everyone safe.
Are magnesium wall boards safe for wet hospital areas?
Facility managers put magnesium wall boards in bathrooms and kitchens. The boards do not let water or mold in. They stay strong in damp places, so they are great for wet hospital areas.
How do magnesium wall boards compare to gypsum boards for fire safety?
Feature | MgO Board | Gypsum Board |
|---|---|---|
Fire Resistance | Up to 4 hours | Up to 2 hours |
Smoke Emission | None | Low |
Magnesium wall boards are better than gypsum boards for stopping fire and smoke.
Do magnesium wall boards require special installation tools?
Tip: Workers use normal hand tools to put up magnesium wall boards. Carbide-tipped blades are best for cutting. People should wear masks and goggles to protect themselves while working.
Can magnesium wall boards help reduce hospital maintenance costs?
Magnesium wall boards do not let mold, water, or bugs in. Hospitals say they fix walls less and the walls last longer. Facility teams spend less money on cleaning and replacing walls over time. 🏥

 Standards and Certifications
Standards and Certifications Installation
Installation