
08 Aug Cement Board Fire Resistance Explained for 2025
Table of Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Fire Resistance Basics
- 3 Cement Board Fire Rating
- 4 Factors Affecting Performance
- 5 Comparison to Other Materials
- 6 Practical Tips
- 7 FAQ
- 7.1 Is cement board completely fireproof?
- 7.2 Can cement board be used behind a wood stove?
- 7.3 How often should cement board be inspected for fire safety?
- 7.4 Does cement board need special fasteners for fire-rated assemblies?
- 7.5 What is the difference between cement board and MGO board for fire safety?
Cement board is not fireproof, but it can resist fire very well. In building, fire resistance means a material can stand up to fire or stop it for a set time. This time is usually counted in hours. Builders and designers use fire ratings to keep people safe and follow the rules. For example, almost 60% of cement board used in commercial buildings in 2025 is because it resists fire. In homes, people use it for fire resistance up to 47%.
Knowing the cement board fire rating helps keep people and things safe. This makes it very important in building today.
Sector | Fiber Cement Board Usage Share in 2025 | Notes on Fire-Resistance Usage |
|---|---|---|
Residential | 35.6% to 47% | Picked for fire resistance and strength |
Commercial | About 60% | Used a lot for fire-resistant buildings |
Key Takeaways
Cement board can stop fire and slow down flames. This helps keep buildings safer. People have more time to get out during a fire. Fire resistance depends on the whole wall or ceiling. It is important to install it the right way. You must also follow building codes. Thicker cement boards protect better from fire. Good installation also helps. Small gaps or using wrong materials can make it less safe. Checking and fixing cement board often keeps it fire-resistant. Fix cracks and damage fast to keep it strong. Cement board is better than drywall at stopping fire. MGO board protects even more but costs more money.
Fire Resistance Basics
Fireproof vs. Fire-Resistant
Some people think “fireproof” and “fire-resistant” mean the same thing, but they do not. In building, experts do not use “fireproof” because nothing can last forever in fire. Even strong things will break down if they get too hot for too long. Instead, people say “fire-resistant” for things that can stop fire for a certain time, like one or two hours.
Fire-resistant things have a rating based on time. For example, a wall with a two-hour rating can stop fire for two hours.
Fireproofing means adding something to help things last longer in fire, but it does not make them safe from all damage.
Fire-resistant things slow down burning and can stop burning when the heat goes away.
Building rules need fire resistance ratings to help keep people safe and give them time to get out during a fire.
Note: “Fireproof” is not always correct. Always look at the fire resistance rating to know how safe something is.
How Cement Board Performs
Cement board is a great pick for fire-resistant building. It does not burn, even if flames touch it. Its non-combustible parts stop fire better than wood, drywall, or fire-rated plywood. Cement board holds heat and slows fire, which helps keep buildings safe in a fire.
Cement board passes hard fire safety tests and gets certified.
Its high thermal mass lets it soak up heat and hold it, so fire spreads slower.
Drywall has gypsum, which can burn if it gets very hot, but cement board stays strong and does not fall apart.
Builders use cement board in places that need a high cement board fire rating, like walls near stoves or fireplaces.
Cement board is strong, lasts a long time, and resists fire, so it is a top choice for safe building in 2025.
Cement Board Fire Rating

Typical Ratings
Cement board fire rating is important for building safety. Most cement board does not burn and gets a Class A fire rating. This means it has a flame spread index from 0 to 25. That makes it good for hospitals, schools, and tall buildings. These places need slow flame spread. ASTM E84 tests show cement board has an FSI of 0. This means it is very good at stopping flames from spreading.
Manufacturers and code officials use UL-classified assemblies to check fire-resistance ratings. The National Gypsum Fire & Sound Assembly Selector lists almost 350 UL fire designs. Some of these designs use cement board. Builders can search by assembly type, fire rating hours, and other things. This helps them pick the right system for their job. USG Durock® Brand Cement Board with EdgeGuard™ is UL Classified. It is approved for any UL Design that lists Type DCB panels.
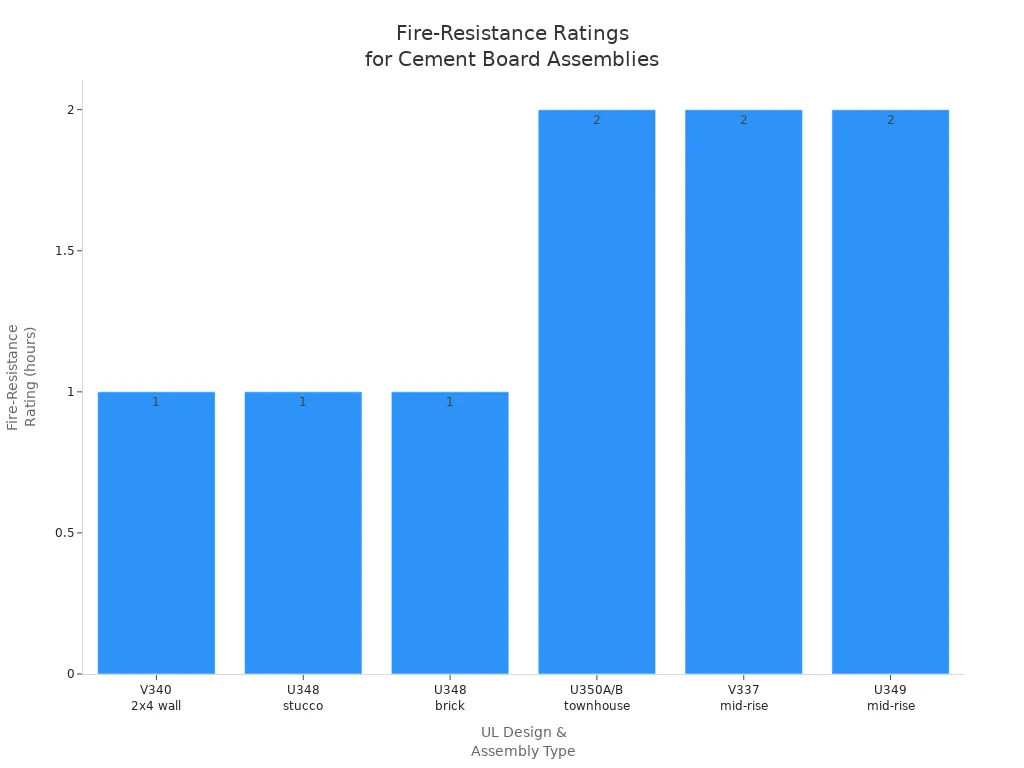
The table below shows common 1-hour and 2-hour fire-resistance ratings for cement board in walls and ceilings:
UL Design No. | Assembly Type | Fire-Resistance Rating | Notes/Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
V340 | 2×4 wall construction | 1-hour both sides | No exterior gypsum required; consistent wall thickness |
U348 (stucco) | Stucco exterior | 1-hour both sides | Common in multifamily Type V construction; allows fiberglass insulation |
U348 (brick) | Brick exterior | 1-hour both sides | Similar to stucco assembly |
U350A, U350B | Townhouse dividing walls | 2-hour fire-resistance | Alternative to shaft wall; conventional framing; STC rating of 61 |
V337 | Mid-rise exterior walls | 1-hour or 2-hour (varies) | 1-hour from either side or 2-hour interior/1-hour exterior; may reduce gypsum layers |
U349 | Mid-rise wall assemblies | 2-hour interior (varies) | Maintains substrate strength; some water-resistive coatings compatible |
These assemblies show that 1-hour fire ratings are common for cement board. You can get 2-hour ratings with more layers or special sheathing.
Assembly Requirements
Cement board by itself does not always give a 1-hour or 2-hour fire rating. The fire rating depends on the whole assembly. This includes framing, insulation, fasteners, and extra layers. All fire-rated assemblies must pass ASTM E119 tests. These tests check how long a wall or ceiling can hold back fire.
The 2025 International Building Code (IBC) puts fire-rated assemblies into three groups. These are fire partitions, fire barriers, and fire walls. Each group has its own rules for how far the wall must go and its fire rating. For example:
Fire partitions can stop at the bottom of a rated floor or roof.
Fire barriers must go all the way up to the floor or roof deck.
Fire walls must go from the ground to above the roof. Sometimes they must go past the outside wall.
Companies like National Gypsum and USG give step-by-step guides for each UL-classified assembly. Builders must follow these guides exactly to get the right fire rating. Even small changes in materials or how you build can change the fire-resistance rating.
Note: Always check the fire-resistance rating of a cement board product. Ask the manufacturer or look at UL documents.
Limitations
Cement board is fire-resistant but not fireproof. It slows down fire and gives people more time, but heat can still move through it. Lab tests show cement board stays strong under medium heat. But if it gets too hot for too long, it gets weaker. For example, fiber-cement boards lose strength over 200°C. At 400°C, the board breaks down in minutes. At 500°C, it can fail in just 1–2 minutes.
Some things can make cement board less effective:
Thickness, density, and what it is made of change fire resistance.
Bad installation makes weak spots that lower protection.
Humidity and temperature changes can make it work worse over time.
Old boards do not resist fire as well, so check and fix them often.
The fire resistance of the whole assembly depends on how well all the parts work together.
Cement board is great for fire resistance in tested assemblies. But you still need good design, careful building, and regular care. Builders should always use cement board as part of a full, code-approved fire-rated system.
Factors Affecting Performance
Thickness and Type
Cement board fire resistance changes with thickness and type. Thicker boards protect better because they heat up slower. They also take longer to break down in a fire. Builders use fiber cement board or cement-bonded particle board for safety. Fiber cement board is strong and lasts a long time. Cement-bonded particle board does not get damaged by water easily. Both types have cement and fibers that do not burn. They also do not let out harmful smoke. This makes them safe near things that get hot. Some products, like PermaBASE Cement Board and PermaBASE PLUS Cement Board, pass tough fire tests. These boards are good for walls behind wood stoves and fireplaces. If you install them right, you can put a stove closer to the wall. The space needed can be up to 40% less. This proves that the right board and thickness are important for fire safety.
Installation Quality
Good installation is very important for fire resistance. Builders must follow the maker’s steps exactly. They put furring strips on wall studs first. Then they attach cement board panels with the correct fasteners. Small air gaps help slow down heat moving through the wall. Covering the surface with tile or stone adds more safety. If builders skip steps or use wrong materials, fire resistance gets worse. Even a small gap or loose screw can make a weak spot. Careful work makes sure cement board works well in a fire.
Maintenance
Taking care of cement board keeps it fire-resistant for years. Checking for cracks or gaps helps find problems early. Fixing damage fast stops fire from getting through. Builders should keep cement board dry and away from big temperature changes. Using rust-proof screws and fireproof sealants keeps joints safe. Adding mineral wool insulation and metal studs makes fire resistance even better.
Maintenance Practice | Description |
|---|---|
Regular Inspections | Check often for cracks or gaps and fix damage fast to keep fire resistance. |
Environmental Protection | Keep away from too much water, high humidity, and sudden temperature changes. |
Proper Installation | Use rust-proof screws, make sure joints are tight, and use fireproof sealants. |
Use of Fire-Resistant Materials | Use cement board with mineral wool insulation and metal studs for better fire resistance. |
Tip: Good care and careful building help cement board last longer and stay fire-resistant.
Comparison to Other Materials
 Drywall
Drywall
Drywall is used a lot in homes and offices. It has a gypsum core, so it can resist fire for a short time. Cement board works better when there is a lot of heat. Cement board does not bend or crack if there is a fire. It stays strong and does not burn. This makes it safer near fireplaces or furnaces.
Material Type | Thickness | Fire Resistance Rating |
|---|---|---|
Cement Board (Durock) | 1/2 or 5/8 inch | |
Standard Drywall | 1/2 inch | About 30 minutes |
Type X Drywall | 1/2 or 5/8 inch | 45 minutes to 1 hour |
Type X drywall is better at stopping fire than regular drywall. But it still does not work as well as cement board. Builders pick cement board for places that need more fire safety.
MGO Board
MGO board is short for magnesium oxide board. It does not burn and is even better at stopping fire than cement board. MGO board can take more heat and does not break down fast in a fire. Builders use MGO board in places where fire is a big risk or where the rules say you need the best fire safety.
Board Type | Fire Performance Description |
|---|---|
MGO Board | Non-combustible, excellent fire resistance, ideal for high-risk areas |
Cement Board | Good fire resistance, may need extra fireproofing in some cases |
MGO board is lighter than cement board and easier to put up. It also does not get damaged by water, mold, or mildew as easily. This helps it last longer.
Choosing the Right Option
Picking the best material depends on a few things:
Fire resistance: MGO board lasts the longest in fire. Cement board is next. Drywall does not last as long.
Installation: MGO board is light and easy to move. Cement board is heavy but very strong.
Moisture resistance: MGO board is best at stopping water damage.
Cost: Cement board costs less at first. MGO board might save money later because it needs less fixing.
Insurance: Using cement board or MGO board can make insurance cheaper.
Environmental impact: MGO board is good for the planet and can be recycled.
Tip: Always look at your local building rules and what your project needs. MGO board is best for fire safety. Cement board is strong and saves money. Drywall is okay for normal use but does not protect as much in a fire.
Practical Tips
Installation Best Practices
Putting in cement board the right way helps stop fires. It also keeps people safe for a long time. Builders should cover open eaves with fiber-cement panels. This makes boxed-in eaves that are safer. Doing this closes gaps and adds a fire-resistant layer. All joints and gaps in siding and eaves need sealing. Use non-combustible caulking for this job. This stops embers from getting inside the building. Non-combustible flashing at roof edges and eaves helps too. It keeps embers out. Builders should use fire-resistant siding instead of wood or vinyl. Good choices are fiber-cement, stucco, or brick. These give more protection. Builders must follow local building codes and wildfire rules. This includes the 2025 codes and California’s WUI Code. Talking to local building departments and insurance companies is smart. This helps builders follow the rules and might give rewards for fire-safe upgrades.
Maintenance Advice
Checking cement board every year keeps it working well. Fire safety codes like NFPA 1 and NFPA 101 say to check fire barriers once a year. Regular checks help find cracks or damage early. This stops fire resistance from getting weaker. Look at cement board siding for wear, especially after storms or changes to the building. Repainting or sealing every 10 to 15 years helps keep it strong. Clean the surface and fix small problems right away. This makes sure the cement board keeps stopping fire.
Watch for signs that cement board is not safe anymore:
Pieces falling off, mostly near the bottom
Board feels weaker or bends too much
Fibers inside the board are gone or melted from heat
If you see any of these, fix or replace the cement board.
When to Consult Experts
Ask fire safety experts or code officials before changing fire protection. Every building has its own risks. Experts need to check these risks. If you have hard code questions or special designs, ask local fire professionals. Builders should get expert help for any fire safety or code questions about cement board. This makes sure the building is safe and follows all the rules.
Cement board will not burn or help fire move. This makes it safer for houses and buildings. It is good for stopping fire in walls and ceilings. This gives people more time to get out if there is a fire. The cement board fire rating depends on putting it in the right way. You must follow the rules for how to build with it. Builders and people who own homes should use the tips in this guide. They should also check local rules or ask experts about fire safety.
Following fire safety rules and using cement board in risky places can lower fire danger and make buildings safer.
FAQ
Is cement board completely fireproof?
Cement board resists fire but does not make a wall fireproof. It slows fire spread and does not burn. Builders must use it in tested assemblies for full protection.
Can cement board be used behind a wood stove?
Yes, cement board works well behind wood stoves. It does not burn or give off smoke. Always follow manufacturer instructions for safe installation.
How often should cement board be inspected for fire safety?
Inspect cement board at least once a year. Look for cracks, gaps, or damage. Fix problems right away to keep fire resistance strong.
Does cement board need special fasteners for fire-rated assemblies?
Use only approved, corrosion-resistant fasteners. Standard screws may not meet fire code. Always check the assembly guide for the correct type.
What is the difference between cement board and MGO board for fire safety?
Feature | Cement Board | MGO Board |
|---|---|---|
Fire Resistance | Very Good | Excellent |
Weight | Heavy | Lighter |
Moisture Proof | Good | Superior |
MGO board offers higher fire and moisture resistance than cement board.
 Drywall
Drywall