
11 Aug The Advantages and Disadvantages of Cement Board in Modern Construction
Table of Contents
You want a building material that can handle water, fire, and bugs. Cement board is strong and lasts a long time. It works well for tile or wet places. But it is heavy and hard to put in, which can slow you down. Many builders now use fiber-cement siding. It does not need much care. It stands up to bad weather and keeps bugs out. Fiber cement siding works in many climates. It does not get ruined by termites. It also keeps looking good for years. Think about the good and bad sides of cement board and fiber cement. This will help you pick what you need. Remember to look at how strong it is, how easy it is to put in, the cost, and if it fits your project before you choose.
Key Takeaways
Cement board is very strong. It does not get damaged by water. It is safe from fire. It is a good base for tile in wet places. It is also good in places where fire can happen.
Fiber-cement siding lasts a long time. It does not get ruined by weather. Bugs cannot harm it. It does not need much care. This makes it good for outside walls.
Both materials are heavy. They need to be handled with care. Skilled workers must install them. This can make labor cost more.
Cement board is best for inside use. It is good for putting tiles on. Fiber-cement siding is better for outside walls. It can look like wood.
You should pick the right material for your project. Think about what you need, your budget, and where you live. Always think about how long it will last. Also think about how easy it is to put in and take care of.
Cement Board Overview
What Is Cement Board
Cement board is not like other building materials. It is a flat, strong sheet. It is made from cement, water, wood fibers, silica, and some special things. These parts make the board tough. They help it fight water, fire, and bugs. There are different kinds of cement board. Each type has its own features. The most common types are:
Wood wool cement boards
Cement bonded particle boards
Wood strand cement boards
Companies use different ways to make these boards. The Hatschek process mixes fibers with cement and makes thin sheets. The extrusion process pushes a thick mix through a mold. Some boards use perlite and are pressed into shape. Additives like silica fume or fly ash make the board stronger and better with water. Wood fibers are dried first so the cement sets right. Pressing and curing the boards takes days. This makes them hard and strong.
Common Uses
Cement backer board is used in many building jobs. It is popular because it works in many places. Here are some common uses:
Bathrooms, kitchens, and showers: Cement backer board is a waterproof base for tile.
Exterior walls and facades: Fibre cement boards protect buildings from bad weather.
Fire-rated assemblies: Cement backer board helps keep walls, ceilings, and floors safe from fire.
High-impact areas: Some boards are good for places that need to be extra strong, like labs or factories.
The table below shows how each type of cement board is used:
Type of Cement Board | Typical Construction Uses | Key Properties and Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Outdoor projects: siding, roofing, cladding | Stands up to water, fire, bugs; lasts in bad weather | |
High-density cement boards | Floors, walls, countertops, commercial spaces | Strong, waterproof, keeps out fire and bugs |
Cement-bonded particleboards | Houses, renovations | Good at keeping heat in, helps lower heating bills |
Cement backer board is strong and can be used in many ways. Fibre cement and cement backer board both last a long time. They help protect buildings and are a smart pick for many jobs.
Cement Board Pros
 Durability
Durability
You want a material that can last a long time. Cement board is very tough and does not break easily. It stays strong even after getting wet and drying many times. The table below shows how cement board does compared to other materials:
Property / Test | Magnesium Oxide (MgO) Cement Board | Gypsum Drywall | Plywood |
|---|---|---|---|
Flexural Strength Retention after 25 Wet/Dry Cycles | Nearly 100% retained | Loses 36-52% strength | Loses 9% strength |
Moisture Absorption | Very low (0.34%) | High absorption | Higher absorption than MgO board |
Mold Growth (ASTM G21 Fungal Test) | No mold growth detected | Mold prone | Mold prone |
Dimensional Stability | No warping, swelling, or delamination | Swelling, crumbling observed | Warping and cupping observed |
Impact Resistance | Very high | Low | Moderate |
Fire Resistance | Non-combustible, flame spread rating 0/0 (ASTM E84), maintains strength >750ºC | Combustible, weaker fire resistance | Combustible, weaker fire resistance |
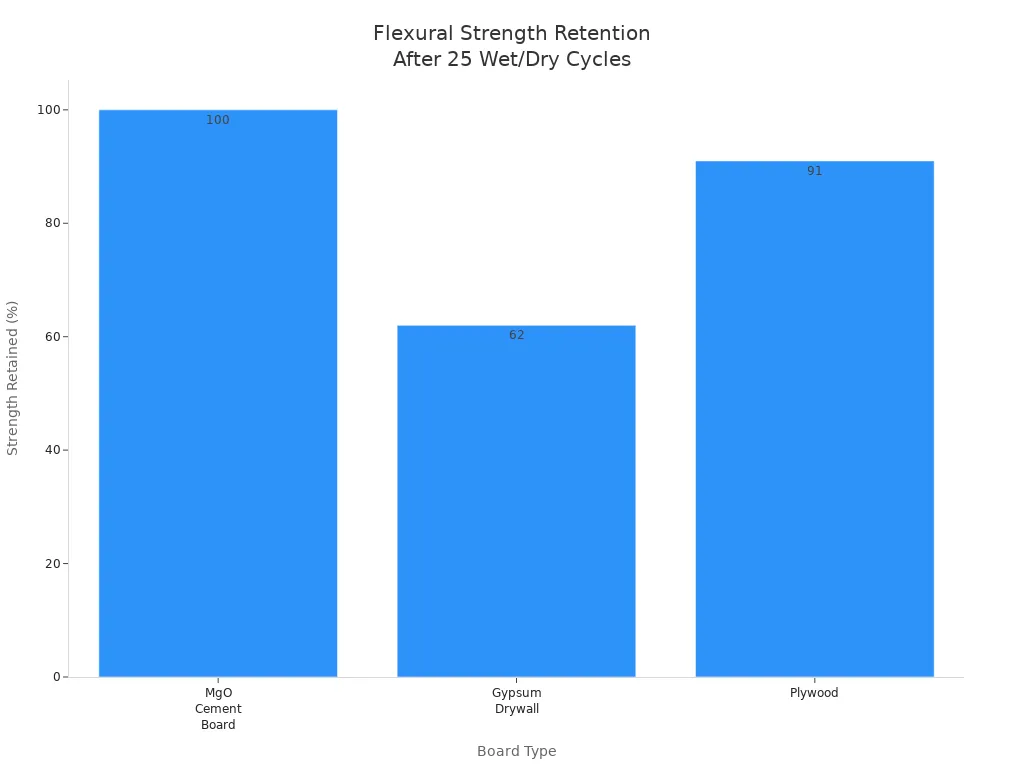
Cement board does not bend, swell, or fall apart when wet. It keeps its shape and stays strong for a long time. This makes it a good pick for places that need to last.
Moisture Resistance
If you need something for wet places, cement board is a great choice. It does not swell, crack, or get weak when it gets wet. You can use it in bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry rooms. Cement backer board keeps its shape and does not let mold grow. Here are some important things to know:
Cement board is very waterproof and does not soak up much water.
It keeps its shape even after being wet for a long time.
Mold and mildew do not grow on cement board easily.
You can use it where water is always around.
You can feel sure your walls and floors will not get ruined by water.
Fire and Pest Resistance
You want your building to be safe from fire and bugs. Cement board gives you strong fire safety. It does not burn or help a fire grow. The board stays strong even when it gets very hot. It also keeps out termites and other bugs. Tests show that cement backer board does not get eaten by termites like wood does. The cement covers the wood fibers, so termites cannot eat them. You get a board that is safe from fire and bugs.
Tip: Use cement board in places where fire safety matters, like kitchens, utility rooms, and outside walls.
Tile and Finish Compatibility
Cement board works well with tile and other finishes. You can put porcelain, ceramic, or stone tiles right on top. The board gives a flat, waterproof base for tile. You can use special cement or epoxy to stick the tiles. For grout, you can use cement grout or epoxy grout. Shiny or rough tiles both work well with cement board. You can also use grout sealer to stop grout from sticking to shiny tiles.
Cement board works with many kinds of tile and finish.
You get a flat, smooth surface for putting down tile.
The board meets the rules for tile and finish use.
Other Benefits and Sustainability
Cement board gives you more than just strength and water safety. It is also good for the environment. Many brands have special labels like Environmental Product Declarations (EPD), GREENGUARD, and Health Product Declarations (HPD). These show that cement board is safe and can be recycled. Some boards use recycled stuff, which helps the planet and green building points. You can feel good about picking a material that helps the earth.
Note: Fibre cement has similar strength, water safety, and bug safety, so both are good picks for today’s buildings.
Cement Board Cons
Weight and Handling
Cement board is much heavier than other building materials. This makes it hard to carry and lift. On big jobs, moving it takes more time and effort. For example, a 5/8-inch PermaBASE cement board weighs about 3.65 pounds per square foot. Gypsum sheathing of the same thickness only weighs 2.5 pounds per square foot. The table below shows how much each material weighs:
Material Type | Thickness | Weight (lbs. per sq. ft.) |
|---|---|---|
Gypsum Sheathing (typical) | 5/8″ | 2.5 |
PermaBASE Cement Board | 1/2″ | 2.9 |
PermaBASE Cement Board | 5/8″ | 3.65 |
PermaBASE CI Insulated Cement | 1″ | 2.2 |
PermaBASE CI Insulated Cement | 2″ | 2.4 |
PermaBASE CI Insulated Cement | 3″ | 2.6 |
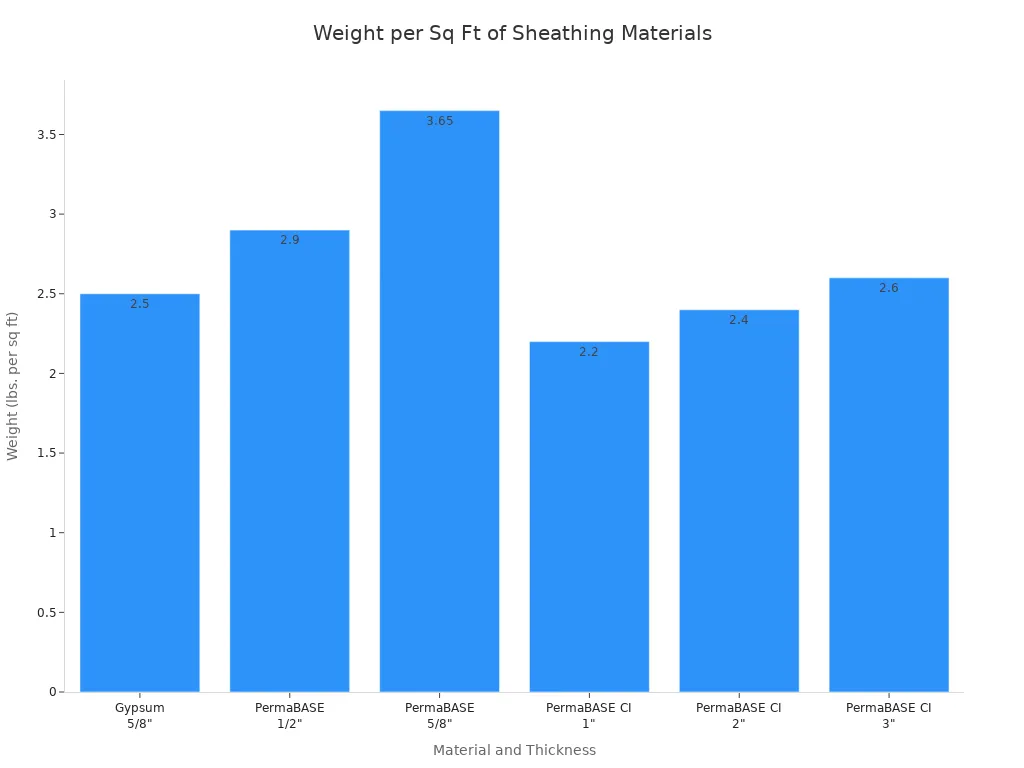
You may need more people to help move and install cement board. The heavy weight can slow down your work. If you work alone or have a small team, it can be tough. Lifting heavy boards can also cause injuries if you do not lift them the right way.
Installation Difficulty
Putting in cement board is not easy. You need special tools to cut it, like saws with dust collectors or power shears. You also need to use nails that do not rust and follow careful steps. The steps for installing cement board often include:
Careful measuring and cutting
Using nail guns or hammers
Putting on caulk and flashing to keep water out
Adding a weather barrier to save energy
Note: Cement board siding is heavier and harder to put up than other siding. You might need more workers or stronger walls.
These steps take more time and skill than putting in drywall or plywood. Because it is harder to install, you may need to hire experts. Labor costs can be 30% to 50% of your total cost. If you try to do it yourself without the right tools, you could break the board or lose your warranty.
Cost
Cement board costs more than many other wall materials. The price is higher because of the material and the extra work needed. Here are some key points about cost:
Cement board costs more to buy and install than drywall.
Labor costs are higher because it is heavy and needs skilled workers.
The total cost is close to other strong materials like magnesium oxide board.
Cement board is better at keeping out water and lasts longer, so you might save money on repairs later.
Drywall is cheaper at first but can cost more over time if it gets damaged.
Tip: Even though cement board costs more at first, it can save you money later because it does not need as many repairs.
Insulation and Flexibility
Cement board does not keep heat in or out very well. It has a low R-value, so it does not help much with insulation. If you want better insulation, you need to use special insulated cement board. The table below shows how thicker insulated cement board gives better R-value:
Thickness of PermaBASE CI Insulated Cement Board | R-Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 inch | R-4 | Good for warm homes; gives some insulation and is strong. |
1-1/4 inch | R-6 | Good for warm businesses; balances insulation and strength. |
2 inches | R-10 | Good for mild areas; higher R-value keeps heat in or out. |
3 inches | R-16 | Good for cold places; best for stopping heat loss. |
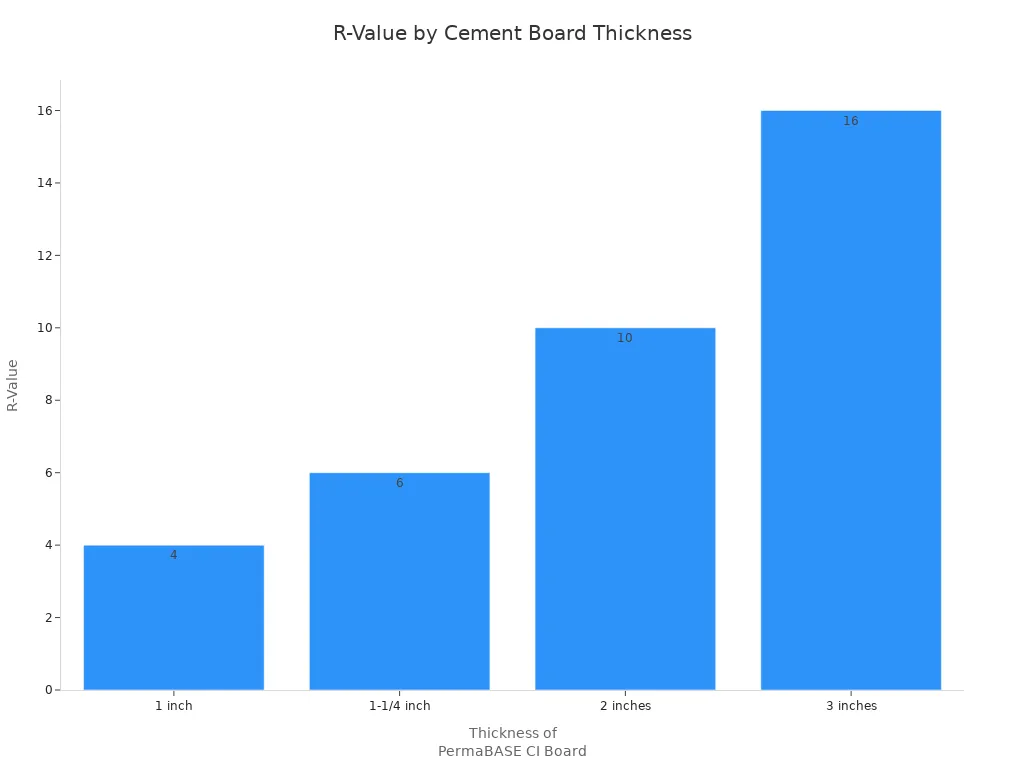
Cement board is stiff and does not bend much. This makes it hard to use on curved walls or places that need bending. You have to plan carefully for corners and edges because it does not flex.
Alert: Cement board should not be used where it is always wet, like in pools or underwater. It also does not work well for some floors that need to move or bend.
Summary of Limitations
Heavy weight makes it hard to move and install.
Cutting and fitting need special tools and skills.
Costs more for both materials and labor than drywall.
Does not insulate well unless you use insulated boards.
Not flexible, so it is hard to use on curves.
Not good for places with constant water or some floors.
You should think about these problems before picking cement board. Knowing the downsides helps you make the best choice for your project.
Fiber-Cement Siding

What Is Fiber-Cement Siding
You can find fiber-cement siding on many new buildings. This material is strong and can bend a little. It is made by mixing Portland cement, sand, water, and cellulose fibers. Some brands add extra things to make it even stronger. The cellulose fibers come from wood pulp. These fibers help stop the board from cracking. They also make it easier to carry and use.
Fiber-cement siding is made with Portland cement, sand or fly ash, water, and cellulose fibers.
Some companies add special things to make it work better.
Cellulose fibers make fiber-cement siding different from regular cement board.
Fiber-cement boards are lighter and can take hits better than cement boards.
You get a strong product that is not too heavy.
If you pick fiber-cement siding, you get something that can handle weather, bugs, and daily use. The way it is made mixes cement and cellulose fibers. This helps the board not crack and makes it easier to put up.
Tip: Fiber-cement siding is a good pick if you want something strong, easy to use, and not too heavy.
Common Applications
Fiber-cement siding can be used in many places. Builders use it for houses, schools, hospitals, and offices. It works in hot, cold, wet, and dry places. Fiber-cement siding stands up to rain, wind, and salty air near the ocean. It also keeps out mold and bugs in damp areas.
Here is a table that shows where fiber-cement siding is used:
Category | Examples / Description |
|---|---|
Climates | Desert (handles heat), Coastal (keeps out rain, wind, salt), Humid (stops mold, bugs), Northern (safe in freezing and thawing) |
Building Types | Schools (easy to care for), Hospitals (lasts long), Office Buildings (handles weather), Theatres (looks nice), Conference Centers (fits everywhere), Retail Buildings (looks good, keeps heat in) |
You can use fiber-cement siding for outside walls, soffits, and some roofs. Fibre cement panels are also good for fancy walls and business buildings. Many architects like fiber-cement siding because it looks clean and lasts a long time.
Note: Fibre cement gives you a strong and nice-looking finish that works almost anywhere.
Advantages of Fiber-Cement Siding
Weather Resistance
You want your home to stand up to harsh weather. Fiber-cement siding gives you strong protection from rain, snow, wind, and sun. This material does not crack or warp when the temperature changes. Hardie fiber-cement siding has passed tough tests for UV rays, snowstorms, and heat. It keeps its shape and strength in all seasons.
A laboratory test measured how well fiber-cement siding holds nails under stress. The test followed ASTM D1037 standards. Panels from three brands showed high resistance to nail pull-through. This means your siding stays secure during storms and high winds.
Test Type | Panel Thickness | Density (kg/m³) | Result: Nail Pull-Through Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
ASTM D1037 (3 brands) | 6.4–7.9 mm | 1310–1680 | High (Panels stayed secure) |
You get lasting protection for your home, even in tough climates. This is one of the main advantages of fiber-cement siding.
Longevity and Low Maintenance
Fiber-cement siding lasts much longer than wood or vinyl. Most brands offer warranties for 30 to 50 years. Some homes keep their fiber-cement siding for over 60 years with proper care. You do not need to paint or repair it often. Wood siding may last only 15 to 20 years. Vinyl siding can fade or crack after 10 to 15 years.
You save time and money because fiber-cement siding is low-maintenance. You do not have to worry about rot, warping, or frequent repairs. This material gives you peace of mind and long-term value.
Tip: Choose fiber-cement siding if you want a product that offers longevity and fewer chores.
Fade and Pest Resistance
Your home’s color stays bright with fiber-cement siding. Hardie Board uses ColorPlus Technology, which bakes the color onto the board. This finish resists fading better than vinyl or wood. If you want a new look, you can repaint fiber-cement siding every 10 to 15 years. Vinyl siding cannot be repainted once it fades.
Fiber-cement siding keeps its color longer than vinyl.
You can repaint it for a fresh look.
It looks like wood but lasts longer.
Fibre cement also keeps pests away. Termites, beetles, and birds cannot eat or damage it. The thick, strong boards stop pests from making holes. You do not get gaps that let insects in, unlike with vinyl or wood. Homeowners who switch to fiber-cement siding often see pest problems disappear.
You get both beauty and protection. These benefits make fiber-cement siding a smart choice for lasting protection and easy care.
Disadvantages of Fiber-Cement Siding
Moisture Absorption Risks
You may think fibre cement is completely waterproof, but it is not. Fiber-cement siding can absorb water if you do not install it the right way. Here are some risks you should know:
Water can get behind fiber-cement siding and cause damage to the wall, insulation, and even the framing.
If you crack the siding during installation, water can enter through those cracks.
Without a good drainage system or rainscreen, moisture can build up behind the siding. This can lead to wood rot, mold, and even structural problems.
Missing flashing or poor details around windows and roofs can let water in, causing rot over time.
Fiber-cement siding can survive floods for a short time, but it will not last if it stays wet for days.
You need to make sure your fiber-cement siding has proper flashing and drainage. Regular checks and maintenance help prevent rot and mold. Even though fibre cement is more waterproof than wood, it still needs care to keep your home safe.
Installation and Labor Costs
You will notice that fiber-cement siding costs more to install than vinyl siding. The material is thicker and harder to cut, so you need skilled workers. The price also depends on your home’s size and design. If you need to remove old siding, the cost goes up.
Siding Type | Cost Per Square Foot | Installation Cost for 2,500 sq ft Home |
|---|---|---|
Fiber Cement | $13,700 – $25,000 | |
Vinyl Siding | $4.50 – $8.20 | $13,325 – $24,300 |
Wood Siding | $6.90 – $13.90 | $19,300 – $45,175 |
Labor for fiber-cement siding is higher than for vinyl because of the extra steps and weight. However, it is less expensive than wood siding, which needs more care and time. You should plan for these costs when choosing fibre cement for your project.
Weight and Handling
Fiber-cement siding is heavy. Each board weighs about 1.67 pounds per square foot. You may need help to lift and move the boards. The weight can slow down your project and make installation harder. Even though you can nail the siding in place, handling the heavy boards takes effort.
Note: Always use safe lifting techniques and ask for help when moving fibre cement boards. This keeps you safe and prevents damage to the siding.
The weight is one of the main limitations of fibre cement. You need to think about this before you start your project. If you want a lighter option, vinyl siding may work better for you.
The disadvantages of fiber-cement siding include moisture risks, higher labor costs, and heavy boards. You must keep up with maintenance to stop rot and mold. Knowing these limitations of fibre cement helps you make the best choice for your home.
Cement Board vs. Fiber-Cement Siding
 Key Differences
Key Differences
Cement board and fiber-cement siding are not the same. Cement board is a board made from cement. It is usually about 3/8-inch thick. People use it under tile, stone, or countertops. Fiber-cement siding is made from sand, Portland cement, cellulose fibers, and water. It comes in panels or planks that look like wood.
Here is a table to help you compare these materials:
Aspect | Cement Board | Fiber-Cement Siding |
|---|---|---|
Composition | Cement-based board, typically 3/8-inch thick | Composite of natural fibers and lightweight concrete |
Typical Use | Backing for tile, stone, fireplaces, countertops | Exterior siding/cladding material |
Durability | Durable, keeps strength when wet or in harsh weather | Rot-proof, fire-resistant, termite-proof, mold resistant, but can warp with moisture |
Maintenance | Needs adhesives like thin-set mortar; low upkeep | Low maintenance, but needs caulking and painting; harder to repair |
Installation | Easy to cut and customize; uses adhesives | Factory-made panels or planks; installed with nails/screws; needs caulking and painting |
Appearance | Functional, not decorative | Mimics wood; many textures and finishes |
Weight | Lighter and easier to handle | Heavier, more difficult to work with |
Weather Resistance | Resistant to damage and weather | Made for exterior use; long lifespan |
Application Focus | Interior or substrate use | Finished exterior cladding |
Fiber-cement siding is made for outside walls. Cement board is best for use inside as a base.
Application Suitability
Pick cement board if you need a strong, flat base for tile. It works well in wet places like bathrooms or kitchens. You can use it behind stone, tile, or as a fire-safe layer. Fiber-cement siding is better for outside walls. It stands up to rain, wind, and bugs. It gives a finished look that can look like wood or other styles.
If you want something for outside, fiber-cement siding protects better and looks nicer. For inside jobs, cement board is the best pick. Fiber cement can also be used for soffits and some panels.
Tip: Always use the right material for your job. Use cement board for tile work. Use fiber-cement siding for outside walls.
Cost Comparison
Cement board usually costs less per square foot than fiber-cement siding. But you need to think about all the costs, not just the board. Putting up fiber-cement siding takes more time and skill, so labor costs are higher. You also need to paint and caulk fiber-cement siding, which adds to the price.
Fiber cement lasts longer outside and needs fewer repairs than wood. Cement board saves money on repairs in wet rooms inside. Both materials are a good value, but you should pick the one that fits your needs.
Note: Plan your budget for both the materials and the work. Pick the product that fits your project and gives you the best results.
Choosing the Right Material
When to Use Cement Board
Pick cement board if you need something strong or fire-safe. It is a good base for tile in wet places like bathrooms or laundry rooms. You can also use it for walls that must stop fire or block noise. Cement board works for many jobs, both inside and outside, even in tough weather.
Here is a table to help you see if cement board is right for you:
Project Condition / Requirement | Why Cement Board is Optimal |
|---|---|
Harsh Environmental Exposure | Resists severe weather, lasts longer, less maintenance |
Fire Resistance Needs | Excellent fire safety for homes and businesses |
Aesthetic and Design Considerations | Smooth finish for visible surfaces |
Acoustic Performance | Absorbs sound, good for quiet spaces |
Budget Constraints | Standard boards suit simple jobs; high-density for tough jobs |
Application Examples | Bathrooms, fire-rated walls, high-traffic areas |
Tip: Choose cement board if you want a strong, safe, and long-lasting base for tile or stone.
When to Use Fiber-Cement Siding
Fiber-cement siding is best for outside walls that need to stay safe from weather, fire, and bugs. Pick this material if your home faces storms, snow, or salty air near the ocean. It is also good if you want a finish that looks like wood but does not need much care.
You can use fiber-cement siding in many places and building types:
Handles cold, snow, and hail without problems
Keeps out fire, bugs, and water
Works well near the ocean if you use stainless steel fasteners
Comes in many colors and styles for a custom look
Fiber-cement siding gives you many choices and works well in tough weather. It helps protect your home and keeps it looking nice for a long time.
Note: Always check local building rules and follow the best ways to install for the best results.
You have learned the main pros and cons of cement board and fiber-cement siding. Each material has unique pros and cons that affect your project. Cement board gives you strength and water resistance, but you must handle its weight and cost. Fiber-cement siding offers weather protection and low upkeep, but you need to watch for moisture risks. Always compare the pros and cons, think about your needs, and talk to a professional if your project is complex.
FAQ
What tools do you need to cut cement board?
You need a carbide-tipped scoring knife, a circular saw with a diamond blade, or power shears. Always wear a dust mask and safety glasses. Cutting outdoors helps keep dust away from your workspace.
Can you paint fiber-cement siding?
Yes, you can paint fiber-cement siding. Use 100% acrylic exterior paint for the best results. Clean the surface first. Let it dry before painting. Many brands offer pre-painted options that last longer.
Is cement board waterproof?
Cement board resists water but does not stop it completely. You should use a waterproof membrane behind the board in wet areas. This keeps your walls safe from leaks and mold.
How long does fiber-cement siding last?
Fiber-cement siding can last 30 to 50 years with proper care. You need to check caulking and repaint every 10 to 15 years. Many brands offer long warranties for extra peace of mind.
Does cement board add insulation to your home?
Cement board alone does not add much insulation. Its R-value is low. If you want better insulation, use insulated cement board or add foam panels behind it.
 Durability
Durability