
26 Jun Insulated Sheathing Board Options for Modern Construction
Table of Contents
Modern building uses new materials to save energy and help the planet. Insulated sheathing boards are important for this change. These boards keep buildings warm, lower energy bills, and support green building methods.
The insulation market is expected to grow from $74.22 billion in 2024 to $119.33 billion by 2032 because of higher demand.
In 2023, U.S. construction spending was $2,023.7 billion. Residential projects made up $866.9 billion. This shows insulated sheathing boards are used a lot in new homes and repairs.
Picking the right insulated sheathing board makes buildings better and helps the environment.
Key Takeaways
- Insulated boards help save energy by keeping heat inside. This lowers energy bills and helps the environment.
- Pick the right board for your project. Think about insulation, water resistance, and fire safety.
- Boards like Polyisocyanurate (PIR) and Magnesium Oxide (MgO) work well for different building needs.
- Using green boards helps the planet and can earn eco-friendly awards like LEED.
- Good insulated boards cost more now but save money later. They cut down on repairs and energy use.
Types of Insulated Sheathing Boards
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) Sheathing Boards
Polyisocyanurate, or PIR, is a top choice for insulation. It works well if you need strong heat resistance. PIR boards have a high R-value, which shows how well they block heat. The National Roofing Contractor’s Association (NRCA) says PIR has an R-value of about R-5.6 per inch in warm areas and R-5.0 per inch in cold places. This makes it great for saving energy in buildings.
PIR boards are also good at resisting fire. They handle fire better than many other materials, making them safer. However, they cost more than other options. If your project focuses on saving energy and safety, the higher price may be worth it.
Tip: Use PIR boards in places needing strong insulation and fire safety, like roofs or walls in extreme weather areas.
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Sheathing Boards
Extruded Polystyrene, or XPS, is tough and resists water well. It keeps its insulation ability even when wet. XPS boards have an R-value of about 5.0 per inch, making them a solid choice for energy-saving projects.
XPS stands out because it doesn’t soak up much water. This helps it stay effective over time. It’s a great pick for areas like foundation walls or basements where moisture is common.
Feature | Performance |
|---|---|
~5.0 | |
Water Absorption Rate | 0.3% |
Density | 1.5 lbs/ft³ |
XPS costs more than EPS but lasts longer and handles dampness better. It’s worth the extra cost in wet areas.
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Sheathing Boards
If you want a cheaper option, Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a good pick. EPS is light, easy to use, and gives moderate insulation with an R-value between 3.6 and 4.2 per inch. It doesn’t insulate as well as PIR or XPS, but it’s popular because it’s affordable.
EPS lets some moisture pass through, which can help in certain cases. But you need to manage moisture carefully to avoid problems like condensation. EPS is often used in walls and floors where saving money and basic insulation are important.
Insulation Type | R-Value per Inch | Water Absorption Rate | Density (lbs/ft³) |
|---|---|---|---|
EPS | 3.6 – 4.2 | 2.0 – 4.0% | 1.0 – 1.5 |
Note: EPS made up over 76% of the market in 2020, showing its popularity in budget-friendly projects.
Each type of insulated sheathing board has its own strengths. Pick one based on your needs for heat resistance, water protection, and cost.
Magnesium Sheathing Boards
Magnesium sheathing boards, also called MgO boards, are strong and useful for modern buildings. Made from magnesium oxide, a natural material, they work well in places needing fire safety, water protection, and strength.
A key feature of MgO boards is that they don’t burn. They can handle high heat without catching fire, making them safer than plywood or OSB (oriented strand board). They also resist water very well. Unlike OSB, which can swell or grow mold when wet, MgO boards stay strong even in damp conditions.
Here’s how MgO boards compare to OSB and plywood:
Feature | MgO Boards | OSB Boards | Plywood |
|---|---|---|---|
Fire Resistance | Doesn’t burn; handles high heat | Burns unless treated | Burns easily; may char |
Moisture Resistance | Resists water, mold, and mildew | Swells and molds when wet | Warps when soaked |
Durability | Very strong; resists impacts | Strong but weakens with water | Strong but can split |
Weight | Light but heavier than OSB | Light and easy to carry | Lighter than MgO; easy to move |
Cost | Costs more but lasts longer | Cheaper but needs more care | Cheaper but needs more care |
Applications | Used for walls, floors, ceilings, outside | Used for floors, roofs, and walls | Used for furniture, floors, and walls |
Eco-Friendliness | Made from natural, recyclable materials | Made from wood; deforestation concerns | Made from wood; deforestation concerns |
MgO boards are great for walls, ceilings, and floors in homes or offices. They also work well outside where weather can be harsh. While they cost more upfront, they last longer and need less fixing, saving money over time.
Tip: Use MgO boards in places with fire risks or high moisture, like kitchens, bathrooms, or outside walls.
Fiberglass-Faced Sheathing Boards
Fiberglass-faced sheathing boards are another good choice for modern buildings. These boards have a gypsum center and fiberglass layers, giving them fire safety, water resistance, and strength.
One big benefit of fiberglass-faced boards is their fire safety. They meet strict fire rules, like the A1 Reaction to Fire standard (BS EN 13501-1) and non-combustibility tests like ASTM E136. This makes them a safe pick for projects needing fire protection.
These boards also fight mold and mildew well. Tests like ASTM D3273 gave them a perfect score of 10 for mold resistance. This makes them ideal for wet places like bathrooms or basements.
Here’s a quick look at their fire and water performance:
Test/Classification | Result |
|---|---|
BS EN 13501-1 | |
Non-combustible | ASTM E136 or CAN/ULC S114 |
Mould Resistance | ASTM D3273 (Score: 10) |
Fiberglass-faced boards are light and simple to install. They are great for new buildings or fixing old ones. Common uses include walls, ceilings, and roofs, especially in places needing fire and water safety.
Note: Fiberglass-faced boards are a better option than regular gypsum boards when you need extra strength and protection from fire and mold.
Benefits of Insulated Sheathing Boards

Energy Efficiency
Insulated sheathing boards help buildings use less energy. They stop heat from escaping in winter and keep spaces cool in summer. This means heating and cooling systems don’t need to work as hard, saving money on energy bills. Materials like Polyisocyanurate (PIR) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) have high R-values, which measure how well they insulate per inch of thickness.
Using these boards improves energy efficiency in homes and buildings. It saves money and lowers your carbon footprint, helping the environment.
Tip: Combine insulated sheathing boards with energy-saving windows and doors for better insulation.
Structural Support
Insulated sheathing boards do more than insulate; they also make buildings stronger. Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) combine foam cores with sheathing layers to act like steel columns. The foam works as the center, while the sheathing adds strength on the sides.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
SIPs | Act like steel columns, adding strength under pressure. |
Analysis | Predicts how SIPs handle compression and bending. |
Real Tests | Confirms how SIPs perform in real-world conditions. |
These boards are great for projects needing insulation and extra strength. They improve durability and stability in construction.
Moisture and Fire Resistance
Insulated sheathing boards protect buildings from water and fire damage. Boards like Magnesium Oxide (MgO) and fiberglass-faced sheathing resist mold and mildew, making them ideal for damp places like basements or bathrooms.
For fire safety, materials like fire-retardant EPS and fiberglass-faced boards meet strict standards. Fire-retardant EPS melts only in small areas, while regular EPS melts more.
Test | Material Type | Fire Classification | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | B-s1, d0 | Slower heat rise in first 4 minutes | |
7 & 8 | Fire-retardant EPS | E | Melts only near damaged spots |
N/A | Standard EPS | F | Melts more than fire-retardant EPS |
Choosing the right board prevents water problems and improves fire safety.
Note: Always check fire ratings to meet building rules.
Sustainability Contributions
Choosing an insulated sheathing board helps create a greener future. These boards cut down the environmental effects of building. They save energy, which reduces greenhouse gases and fights climate change.
Many boards use materials that can be recycled or reused. For instance, Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) can often be used again. This lowers waste and saves resources. Some boards, like Magnesium Oxide (MgO), are made from natural materials, making them eco-friendly.
These boards also save energy over a building’s life. Better insulation means heating and cooling systems work less. This saves energy and cuts utility bills. Over time, the energy saved balances out the cost of making the boards.
Some boards meet green building certifications like LEED. These certifications show the materials follow strict eco-friendly rules. Using certified boards can make your project more sustainable and valuable.
Tip: Pick brands that focus on eco-friendly practices, like using recycled materials or cutting carbon emissions.
By choosing the right insulated sheathing board, you help the planet and build stronger, energy-saving structures.
Applications of Insulated Sheathing Boards
Residential Construction
Insulated sheathing boards help homes stay warm or cool. They stop heat from moving through walls, making rooms comfortable. This also lowers heating and cooling costs. Cold places, like zones 6, 7, and 8, need more insulation. Walls there should have R-30 or R-20 plus an extra R-5 layer. Warm areas, such as zones 1 and 2, need less insulation, sometimes as low as R-13.
Climate Zone | Wall Insulation Needed |
|---|---|
6, 7, 8 | R-30 or R-20 + R-5 |
4, 5 | R-20 + R-5 or R-13 + R-10 |
3 | R-20 or R-13 + R-5 |
1, 2 | R-13 or R-0 + R-10 |
Picking the right board helps meet these needs. It saves money and helps the planet by using less energy.
Commercial and Industrial Buildings
These boards are useful in big buildings like offices or factories. They save energy and make walls and roofs stronger. This is important for large structures. Boards like fiberglass-faced ones are good for fire safety. They also resist mold, which is helpful in damp places like storage rooms.
Using insulated boards can meet strict building rules. They improve safety and keep spaces dry and protected.
Retrofitting Older Structures
Older buildings can waste a lot of energy. Adding insulated boards can fix this problem. In the U.S., buildings use 39% of all energy, and homes use 20%. Many homes—68%—were built before 1992 and lack good insulation.
Fact | Number |
|---|---|
Energy used by U.S. buildings | 39% |
Energy used by homes | 20% |
Homes built before 1992 | 68% |
Homes with no wall insulation | 34.5 million |
Single-family homes without insulation | 38% |
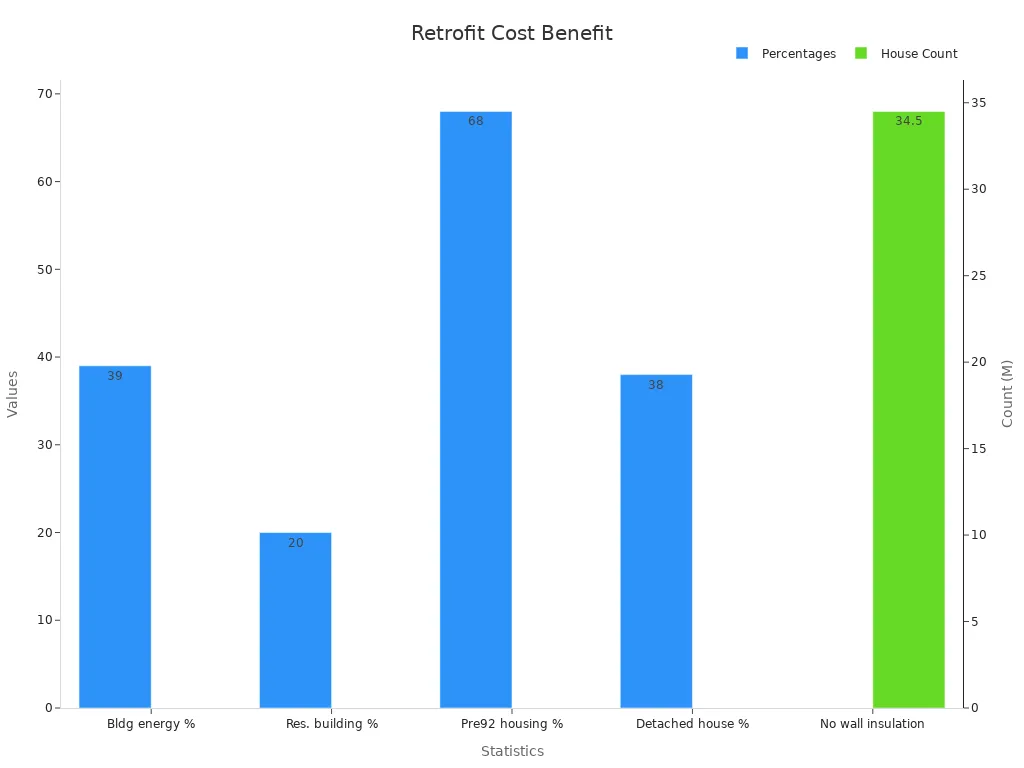
Adding insulation to older homes stops energy loss. It makes homes more comfortable and lowers heating and cooling costs. Retrofitting is a smart way to save money and make old buildings last longer. It also helps the environment by reducing energy use.
High-Performance and Green Building Projects
High-performance and green buildings focus on saving energy and helping the planet. Insulated sheathing boards are important for reaching these goals. They keep heat inside, use less energy, and make indoor spaces more comfortable.
Fiberboard sheathing is great for green building. It has an R-value of 2.5 per inch. This is much better than OSB and plywood, which have R-values between 0.5 and 0.62. The higher R-value keeps rooms warm or cool, so heating and cooling systems work less. Using fiberboard for continuous insulation stops heat from escaping through the frame. This makes it a smart choice for energy-saving homes.
Tip: Choose fiberboard sheathing to save energy and lower costs in green projects.
Green buildings often use insulated sheathing boards to meet eco-friendly standards. These boards help earn certifications like LEED by cutting energy use and supporting green practices. They also improve air quality by stopping drafts and keeping temperatures steady indoors.
Material | R-Value per Inch | Application |
|---|---|---|
Fiberboard Sheathing | 2.5 | Energy-saving homes |
OSB | 0.5 – 0.62 | Basic building projects |
Plywood | 0.5 – 0.62 | General construction use |
Picking the right insulated sheathing board helps build energy-efficient and eco-friendly structures. These buildings save money over time and protect the environment.
Cost Considerations for Insulated Sheathing Boards
Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Savings
Think about both upfront costs and future savings when picking insulated sheathing boards. Different types of insulation have different starting prices:
- Fiberglass costs $0.50–$1.75 per square foot.
- Blown-in cellulose costs $1.00–$2.00 per square foot.
- Spray foam is pricier at $1.50–$5.00 per square foot.
Spray foam costs more at first but saves money later. It can lower energy bills by 15–30%, saving $200–$600 yearly. Over time, these savings cover the initial cost. Payback times differ: fiberglass takes 2–4 years, cellulose 3–5 years, and spray foam 5–7 years. Insulation lasts 20–80 years, saving money as energy prices rise 3–5% yearly.
Tip: Check how long it takes to recover your costs for better planning.
Price Variations by Material Type
The price of insulated sheathing boards changes based on the material. Here are some examples:
Material Type | Cost Variation |
|---|---|
Timber/Lumber | Changes |
Plywood | Changes |
Gypsum | Changes |
Marble | Changes |
Glazed Ceramic Tiles | Changes |
Oriented Strand Boards (OSB) | Changes |
Others | Changes |
Prices depend on things like availability and demand. OSB might be cheaper in areas with lots of timber. Gypsum could cost less where it’s made locally.
Factors Influencing Costs
Many things affect the price of insulated sheathing boards. Thicker boards insulate better but cost more. Boards with higher R-values block heat better but are pricier.
Brand reputation also matters. Famous brands charge more because they’re trusted. Market trends can change prices too. The market for these boards may grow from $13.51 billion in 2024 to $16.88 billion by 2030. Higher demand could make prices go up or down.
Note: Compare brands and materials to find the best mix of cost and quality for your needs.
Choosing the Right Insulated Sheathing Board
Evaluating Project Needs
To pick the best insulated sheathing board, think about your project’s needs. What do you want the board to do? Is it for insulation, strength, or keeping out moisture? Different boards have different strengths. For example, Polyisocyanurate (PIR) boards are great for keeping heat in. Magnesium Oxide (MgO) boards are strong and resist fire well.
Also, think about where the board will go. Outside walls need to handle tough weather. Inside walls might need fire safety or soundproofing. Check the R-value too. A higher R-value means better insulation, which helps save energy.
Tip: Write down what your project needs, like insulation or safety. This will help you choose the right board.
Climate and Environmental Factors
Your local weather affects which board is best. In cold places, use boards with high R-values to keep heat inside. PIR and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) boards work well in these areas. In hot places, pick boards that block heat from coming in.
If your area is wet or humid, choose boards that resist water and mold. XPS and fiberglass-faced boards are good because they stay strong even when wet.
Think about the environment too. Some boards, like MgO and fiberboard, are eco-friendly. They help lower your building’s carbon footprint and meet green building rules.
Note: Always check your local building rules and climate needs before picking a board.
Material Compatibility
Make sure the board works well with other materials in your project. Some boards fit better with certain wall types or finishes. For example, EPS boards work well with stucco or siding. MgO boards are good for tile or stone finishes.
Think about how the board fits with your building’s frame. Rigid boards like XPS and PIR add strength and work well with wood or steel frames. Flexible boards like EPS might need extra support during setup.
Also, consider how easy the board is to install. Lightweight boards, like fiberglass-faced ones, are simple to cut and handle. This makes them great for fixing older buildings.
Tip: Ask your contractor or supplier to make sure the board matches your materials and design.
Budget and Value Assessment
Picking the right insulated sheathing board means balancing cost and value. Some boards may cost more at first but save money later. To choose wisely, think about these points:
Upfront Costs
Look at how much the board costs to buy. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is cheaper and good for tight budgets. Boards like Polyisocyanurate (PIR) or Magnesium Oxide (MgO) cost more but offer better insulation and last longer. If your budget is small, pick a board that meets basic needs without overspending.Long-Term Savings
Think about how much money you’ll save over time. Boards like Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) lower energy bills by keeping heat in or out. This means your heating and cooling systems work less, saving money monthly. Spending more on a high R-value board now can save 20–30% on energy costs later.Durability and Maintenance
Some boards last longer and need fewer repairs. Magnesium Oxide (MgO) boards resist fire, water, and mold, cutting down on repair costs. Fiberglass-faced boards also handle tough conditions well. Choosing a strong board means fewer replacements and lower long-term costs.Project-Specific Needs
Match the board to your project’s needs. In wet areas, use a board like XPS that resists water. For fire safety, pick MgO or fiberglass-faced boards. Choosing the right board for your project ensures you get the most value.Environmental Impact
Some boards are eco-friendly and reduce waste. Boards like MgO or EPS are recyclable or made from natural materials. Using green materials can help you earn certifications and increase your property’s value.
Tip: Compare the board’s cost with how long it lasts and performs. Spending a bit more now can save money and give better results later.
By thinking about your budget and what each board offers, you can make a smart choice. The right board saves money, improves comfort, and makes your building more efficient.
Insulated sheathing boards bring many benefits to modern buildings. Types like Polyisocyanurate (PIR) have high R-values for better insulation. Magnesium Oxide (MgO) boards are great for fire safety. These boards save energy, lower carbon emissions, and make structures stronger.
Choose the right board based on your project’s needs. In cold areas, use materials like PIR with high R-values. For wet places, pick water-resistant boards like Extruded Polystyrene (XPS). Think about the environment too. Boards like INS-PCM5 cut carbon emissions a lot, as shown below:
Region | Insulation Type | Carbon Emission Reduction (kg-CO2/m2) | PCM Advantage (kg-CO2/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | INS | 11.6 | 11 |
1 | INS-PCM5 | 26.58 | N/A |
2 | INS | 24.25 | 18.1 |
2 | INS-PCM5 | 42.36 | N/A |
3 | INS | 31.6 | 15.9 |
3 | INS-PCM5 | 47.5 | N/A |
4 | INS | 40.37 | 13.3 |
4 | INS-PCM5 | 53.68 | N/A |
Using insulated sheathing boards saves energy and helps the planet. They cut utility bills and fight climate change. Pick eco-friendly boards to build a better future.
FAQ
What is the best insulated sheathing board for cold climates?
Pick boards with high R-values like Polyisocyanurate (PIR) or Extruded Polystyrene (XPS). These boards trap heat and stop energy loss. They are perfect for freezing weather.
Tip: Find out your climate zone to know the insulation level you need.
Can insulated sheathing boards be used for retrofitting older homes?
Yes, they make older homes more energy-efficient. They stop heat from escaping through walls and roofs. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a budget-friendly choice for retrofits.
Note: Adding insulation can cut energy costs and make homes cozier.
Are insulated sheathing boards eco-friendly?
Many boards, like Magnesium Oxide (MgO) and Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), are recyclable or made from natural materials. They save energy and lower carbon emissions, helping green building efforts.
Material | Eco-Friendly Features |
|---|---|
MgO | Natural, recyclable |
EPS | Recyclable, energy-saving |
How do I choose the right board for my project?
Think about your needs. For fire safety, go with Magnesium Oxide (MgO). For water resistance, pick Extruded Polystyrene (XPS). Match the R-value to your climate for the best insulation.
Tip: Talk to a contractor to ensure the board works with your materials.
Do insulated sheathing boards save money in the long run?
Yes, they lower heating and cooling costs by improving insulation. Boards like PIR and XPS can save up to 30% on energy bills each year.
Emoji Insight: 💡 Good insulation means smaller bills and a more comfortable home.
